- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Multispecialty
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
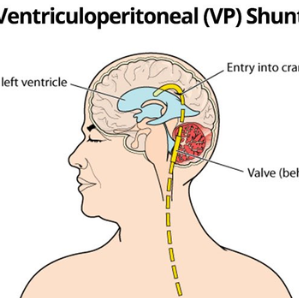
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt (VP Shunt)
A Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt (VP
Shunt) is a surgical procedure designed to alleviate increased intracranial
pressure caused by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the brain's
ventricles. This condition, known as hydrocephalus, can occur due to various
reasons, such as congenital malformations, tumors, infections, or bleeding. The
VP Shunt is a device that diverts excess CSF from the brain to the peritoneal
cavity, where it can be absorbed by the body. Here are key aspects of VP Shunt
placement:
CSF Diversion: The primary purpose of a VP Shunt is to redirect
excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain's ventricles to another part of the
body where it can be absorbed, preventing an increase in intracranial pressure.


.png)