- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Multispecialty
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
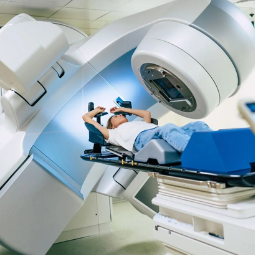
Radiation Therapy
Radiation Therapy, also known as radiotherapy, is a medical treatment modality that uses
high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancer cells or to prevent their
growth. It is a common and highly effective treatment approach for various
types of cancer. Radiation therapy can be administered externally or
internally, depending on the specific cancer, its location, and the treatment
plan developed by the healthcare team.
Here are some key points about radiation therapy:
Purpose: Radiation
therapy is used for several purposes, including curative intent (with the goal
of completely eradicating cancer), adjuvant therapy (used after surgery or
other treatments to eliminate any remaining cancer cells), and palliative care
(to relieve symptoms or slow the progression of advanced cancer).
External Beam Radiation: In this method, a machine outside the body delivers precisely targeted
radiation beams to the cancer site. It is a non-invasive procedure and is the
most common form of radiation therapy.
Internal Radiation (Brachytherapy): In this method, radioactive sources are placed directly inside or very
close to the tumor. This is often used for certain types of cancers, such as
cervical, prostate, and gynecological cancers.
Fractionation: Radiation therapy is usually administered in multiple sessions
(fractions) over a period of several weeks. This approach allows for the
targeted destruction of cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy
surrounding tissue.
Simulation and Planning: Before treatment begins, a patient undergoes a simulation process to
precisely determine the treatment area and the best angles for radiation
delivery. Treatment plans are customized for each patient to maximize the
effectiveness and minimize side effects.
Side Effects: Common
side effects of radiation therapy can include skin changes, fatigue, nausea,
and discomfort in the treated area. The type and severity of side effects can
vary depending on the type of radiation therapy, the location of the treatment,
and the individual patient.
Combination Therapy: Radiation therapy is often used in combination with other cancer
treatments, such as surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy,
to improve outcomes.
Radiation Oncologist: A radiation oncologist is a medical doctor who specializes in the use
of radiation therapy to treat cancer. They work closely with a team of
healthcare professionals to develop and oversee the treatment plan.
Follow-up: Patients
receiving radiation therapy are closely monitored throughout and after
treatment to assess its effectiveness and manage any side effects. Follow-up
care is an essential part of the treatment process.
Radiation therapy is a valuable tool in the fight against cancer and can
be used to treat various cancer types, including breast, lung, prostate, head
and neck, and many others. The choice of radiation therapy as part of a
patient's treatment plan depends on the specific cancer diagnosis and stage, as
well as individual factors like overall health and treatment goals. Patients
should have open discussions with their healthcare team to understand the role
of radiation therapy in their cancer care.






.png)