- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Multispecialty
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
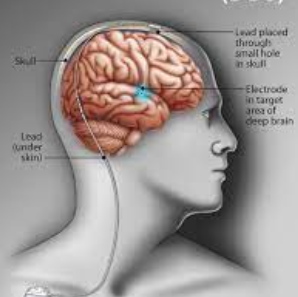
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure that involves the
implantation of a device, often referred to as a "brain pacemaker,"
to deliver electrical impulses to specific areas of the brain. The primary
purpose of DBS is to modulate abnormal neural activity and alleviate symptoms
associated with certain neurological and movement disorders.
Symptom Management: DBS is used to manage symptoms of various
neurological conditions, particularly movement disorders characterized by
abnormal brain activity.
Conditions Treated with DBS:
Parkinson's Disease: DBS is commonly used to treat symptoms such as tremors, stiffness, and bradykinesia (slowness of movement) in individuals with Parkinson's disease.
Essential Tremor: DBS is effective in reducing or eliminating tremors associated with essential tremor.
Dystonia: DBS is used to manage symptoms of certain forms of dystonia, a movement disorder characterized by sustained muscle contractions.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: In some cases, DBS is explored as a treatment for severe, treatment-resistant OCD.


.png)