- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Multispecialty
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
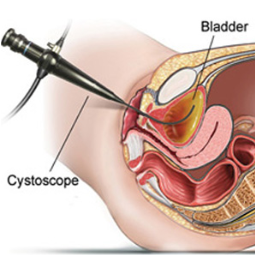
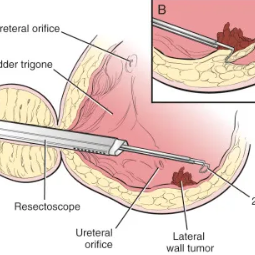
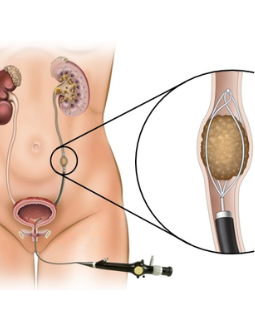
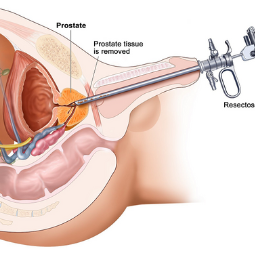
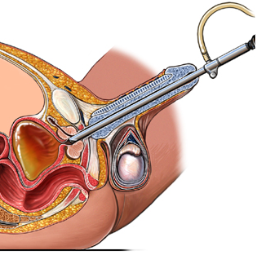
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is a
medical procedure that involves the use of a cystoscope, a thin, flexible tube
with a camera and light on the end, to examine the interior of the urinary
bladder and urethra. Cystoscopy is a common diagnostic and sometimes
therapeutic procedure in urology. Here's what you need to know about
cystoscopy:
Purpose:
Cystoscopy is used to diagnose and evaluate a variety of urological conditions,
including but not limited to:
- Investigating urinary tract symptoms, such as blood in the urine, frequent urination, or pain during urination.
- Identifying the cause of urinary incontinence or recurrent urinary tract infections.
- Detecting and evaluating bladder tumors, stones, or other abnormalities.
- Guiding certain treatments and procedures, such as the removal of bladder stones or the placement of urinary catheters.
Types of Cystoscopy:
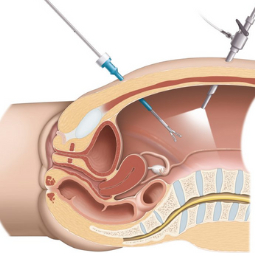
- Flexible Cystoscopy: In this type, a thin, flexible cystoscope is used, often without the need for anesthesia. It is typically used for routine diagnostic purposes and can be performed in an outpatient setting.
- Rigid Cystoscopy: This
method uses a slightly larger, rigid cystoscope and is often used when
more extensive procedures are required. General or regional anesthesia may
be administered in this case.
Procedure: During the cystoscopy, the urologist will insert the cystoscope through the urethra and into the bladder. The camera on the cystoscope allows the urologist to visually inspect the lining of the bladder and urethra. If necessary, the urologist can take biopsies, remove small growths or stones, or perform other minor procedures during the cystoscopy.
Anesthesia: For a flexible cystoscopy, local anesthesia
or a numbing gel may be used to reduce discomfort during the procedure. Rigid
cystoscopy, if performed under general or regional anesthesia, is often
associated with less discomfort.
Recovery: Recovery after a flexible cystoscopy is
typically quick, with patients able to return to their usual activities shortly
after the procedure. Rigid cystoscopy, especially if done under general
anesthesia, may have a longer recovery period.
Risks and Complications: While
cystoscopy is generally safe, there can be some risks, including the
possibility of infection, bleeding, discomfort, or injury to the urinary tract.
It's essential to discuss the procedure with your urologist, understand
the reason for it, and any potential risks or complications that may be
involved. Cystoscopy is a valuable tool in diagnosing and managing urological
conditions, and it can provide valuable information for the assessment and
treatment of various urinary tract and bladder problems.


.png)