- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Ayurvedic Treatment
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
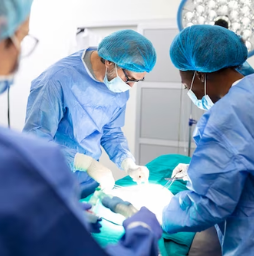
Surgical Resection
Surgical
Resection,
also known simply as "resection," is a medical procedure that
involves the surgical removal of a part of an organ, a tissue mass, or a
structure within the body, typically to treat a medical condition or disease.
In the context of oncology, surgical resection is often used to remove
cancerous tumors or tissue that has been affected by cancer. The primary goal
of this procedure is to eliminate or reduce the cancer's presence within the
body.
Key
points about surgical resection in oncology:
Purpose: Surgical resection
is used to remove cancerous tumors or tissue that may include primary tumors
(the original site of the cancer) or metastatic tumors (tumors that have spread
from the primary site to other parts of the body).
Types: Surgical resections can vary in
scope and invasiveness, ranging from minimally invasive procedures, such as
laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery, to more extensive open surgeries.
Curative or Palliative: Surgical resection
may be performed with curative intent when the goal is to completely remove the
cancer and provide the best chance of cure. In some cases, it may also be
performed with palliative intent to relieve symptoms or improve the patient's
quality of life, even when complete cure is not possible.
Resectable vs. Unresectable: The feasibility of
surgical resection depends on the tumor's location, size, and extent. Tumors
that can be completely removed with surgery are called "resectable,"
while those that cannot be entirely removed are termed
"unresectable."
Risk and Benefits: Surgical resection
carries risks associated with any surgery, such as infection, bleeding, and
anesthesia-related complications. However, it can offer the benefit of
immediate removal of cancerous tissue.
Follow-up Treatment: Surgical resection
is often combined with other treatments, such as radiation therapy,
chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy, depending on the specific
cancer type and stage. This comprehensive approach is aimed at increasing the
likelihood of long-term success.
Recovery: The recovery
period after surgical resection varies depending on the complexity of the procedure
and the patient's overall health. Patients may require postoperative care and
rehabilitation.
Surgical
resection is a common and important component of cancer treatment. It is
typically performed by surgical oncologists who specialize in cancer surgery.
The decision to proceed with surgical resection is made based on various
factors, including the type and stage of cancer, the patient's overall health,
and the potential benefits and risks associated with the procedure. Patients
should have a thorough discussion with their medical team to understand the
details of the surgery and the overall treatment plan.






.png)