- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Multispecialty
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
Kidney Biopsy
Kidney Biopsy is a medical procedure performed to obtain a small sample of kidney
tissue for diagnostic purposes. It is typically conducted when there is a need
to investigate and determine the cause of kidney disease, assess the extent of
kidney damage, or guide treatment decisions. Kidney biopsy provides valuable
information that helps healthcare professionals make accurate diagnoses and
develop appropriate treatment plans for patients with kidney conditions.
Here's an
overview of kidney biopsy:
Purpose: The primary purpose of a kidney biopsy is to
obtain a tissue sample from the kidney for analysis. This sample is examined by
a pathologist under a microscope to diagnose the underlying kidney condition
and determine the best treatment approach.
Procedure:
- Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient's medical history, medications, and coagulation (blood clotting) status are evaluated. Blood tests and imaging studies may be performed to assess the kidney's anatomy and function.
- Anesthesia: Kidney biopsy is usually performed under local anesthesia. The patient may be given a sedative to help them relax during the procedure.
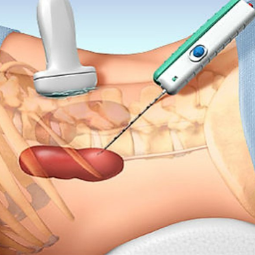
- Guidance: The procedure is guided by ultrasound or, less commonly, by computed tomography (CT) or fluoroscopy to ensure that the needle is accurately placed in the kidney.
- Biopsy: A thin, hollow needle is inserted through the skin and muscle and into the kidney to obtain a small tissue sample. The procedure is typically guided by real-time imaging to target the area of interest. The needle is quickly and carefully inserted and withdrawn to minimize the risk of complications.
- Sample Collection: The
collected kidney tissue sample is then sent to a pathology laboratory for
analysis.
Recovery: After the kidney biopsy, patients are
typically observed for several hours to ensure that there are no immediate
complications, such as bleeding or pain. Patients may be required to lie flat
and remain still for some time to reduce the risk of bleeding. Most patients
can go home the same day.
Risks and Complications: Kidney
biopsy is generally considered a safe procedure, but there are potential risks,
including bleeding, pain, infection, and injury to nearby organs. Patients are
closely monitored after the biopsy, and they are given instructions on
post-procedure care and follow-up.
Diagnosis and Treatment: The
results of the kidney biopsy are essential for diagnosing various kidney
conditions, such as glomerulonephritis, interstitial nephritis, kidney
infections, and other kidney diseases. Based on the diagnosis, healthcare
providers can develop an appropriate treatment plan, which may include
medications, dietary modifications, or other interventions.
Kidney biopsy is typically performed by a nephrologist or interventional
radiologist with expertise in the procedure. It is a valuable tool for
diagnosing and managing a wide range of kidney diseases, and its benefits in
guiding treatment decisions often outweigh the associated risks. Patients
should have a detailed discussion with their healthcare provider to understand
the procedure, potential risks, and benefits before undergoing a kidney biopsy.


.png)