- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Ayurvedic Treatment
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
Neuro-endoscopy
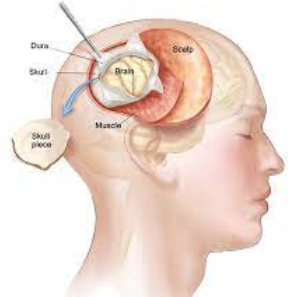
Neuro-endoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that
involves the use of an endoscope to visualize and treat conditions within the
brain, ventricles, or subarachnoid space. The endoscope is a thin, flexible
tube with a light source and a camera at its tip, allowing neurosurgeons to
access and navigate through narrow or deep structures in the brain. Neuro-endoscopy
is used for diagnostic purposes as well as for treating various neurological
conditions.
Purpose:
Visualization and Treatment: Neuro-endoscopy enables surgeons to visualize and
access areas within the brain and surrounding structures.
Minimally Invasive: The procedure is considered minimally invasive
compared to traditional open surgery, as it typically involves smaller
incisions.
Indications for Neuro-endoscopy:
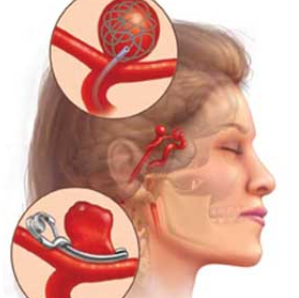
Ventricular Conditions: Neuro-endoscopy is commonly used for procedures
involving the ventricular system, such as the third ventricle or lateral
ventricles.
Cyst Removal: Neuro-endoscopy can be used to remove cysts or
tumors located within the brain.
Hydrocephalus Treatment: In some cases of hydrocephalus (accumulation of
cerebrospinal fluid), neuro-endoscopy may be employed to create a communication
pathway or perform fenestration to relieve fluid buildup.
Tumor Biopsy: Neuro-endoscopy can be used to obtain biopsies of
tumors within the brain.


.png)