- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Multispecialty
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
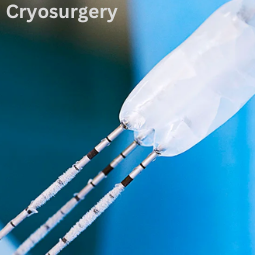
Cryosurgery
Cryosurgery, also known
as cryotherapy or cryoablation, can be used as a treatment option for certain
types of cancer. It involves freezing and destroying cancerous tissue by
exposing it to extremely cold temperatures. Cryosurgery is most commonly
employed for localized, small, or superficial tumors, and it may be used as a
primary treatment or as part of a multimodal treatment plan, depending on the
specific type and stage of cancer.
Here
are some key points about cryosurgery for cancer:
Suitable Cancers:
Cryosurgery is typically considered for cancers that are confined to a
well-defined and accessible area. Common types of cancer that may be treated
with cryosurgery include:
Prostate Cancer:
Cryosurgery is often used to treat localized prostate cancer, particularly in cases
where other treatment options may not be suitable.
Liver Cancer:
Cryoablation can be used for small liver tumors, either as a primary treatment or
in combination with other therapies.
Kidney Cancer: Small
renal cell carcinomas or kidney tumors may be treated with cryosurgery.
Skin Cancer:
Superficial skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are
often treated with cryosurgery.
Lung Cancer: In some
cases, cryoablation may be used to treat lung tumors that are difficult to
access through traditional surgery.
Procedure: During cryosurgery for cancer,
a cryoprobe or cryo-applicator is placed in or near the tumor. The probe is
cooled to extremely low temperatures using a cryogen, typically liquid nitrogen
or argon gas. The freezing process destroys the cancer cells by forming ice
crystals within them.
Effectiveness:
Cryosurgery can be an effective treatment for small, localized tumors. Its success
depends on factors such as tumor size, location, and the type of cancer.
Cryosurgery is generally considered curative for some early-stage cancers.
Advantages: Cryosurgery has certain
advantages, such as minimal invasiveness, reduced risk of complications,
shorter recovery times, and the ability to perform the procedure in an
outpatient setting.
Side Effects: Common
side effects of cryosurgery may include localized pain, swelling, redness, and
blistering at the treatment site. These effects are usually temporary and
resolve during the healing process.
Complications: While
cryosurgery is generally safe, complications can occur, such as damage to
nearby healthy tissues, infection, and recurrence of the cancer.
Follow-Up: Regular follow-up and
monitoring are essential after cryosurgery to assess treatment effectiveness,
watch for any recurrence, and address any potential complications or side
effects.
It's
important to note that the suitability of cryosurgery as a cancer treatment
varies depending on the individual patient, the type and stage of cancer, and
the tumor's location. Patients should have comprehensive discussions with their
healthcare team to understand the potential benefits and risks of cryosurgery
for their specific cancer diagnosis.






.png)