- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Multispecialty
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
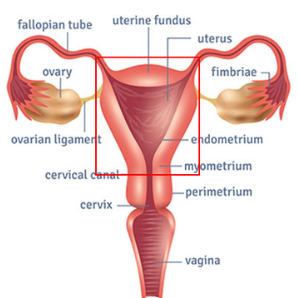
Hysterectomy
A hysterectomy is a surgical
procedure that involves the removal of the uterus. Depending on the specific
type of hysterectomy, other reproductive organs such as the cervix, ovaries,
and fallopian tubes may also be removed. Hysterectomy is a common and major
surgical procedure that can be performed for various medical reasons.
Purpose:
Medical Conditions: Hysterectomy may be recommended for various
medical conditions, including:
- Uterine fibroids (noncancerous growths in the
uterus).
- Endometriosis (a condition where tissue similar to
the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus).
- Uterine cancer.
- Chronic pelvic pain.
- Abnormal bleeding that does not respond to other
treatments.
- Prolapsed uterus (when the uterus descends into the
vaginal canal).
Types of Hysterectomy:
Total Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus and cervix.
Subtotal or Partial Hysterectomy: Removal of the upper part of the uterus, leaving the cervix intact.
Radical Hysterectomy: In addition to the uterus and cervix, nearby
tissues such as the upper part of the vagina and supporting ligaments may be
removed. This is typically done for certain gynecological cancers.


.png)