- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
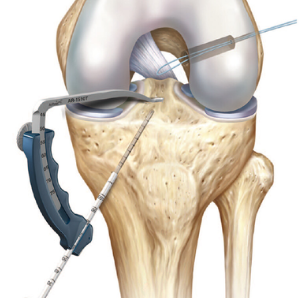
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
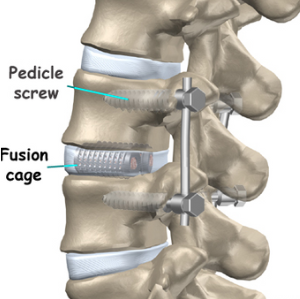
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Ayurvedic Treatment
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
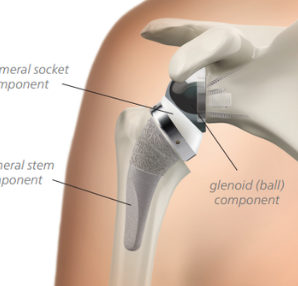
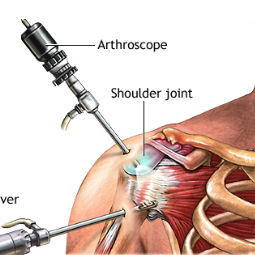
Total Shoulder Replacement
Total Shoulder Replacement, also known as Total Shoulder Arthroplasty,
is a surgical procedure in which the damaged or diseased parts of the shoulder
joint are replaced with artificial components. This procedure is often
recommended for individuals with severe shoulder arthritis or other conditions
that cause pain and limited function in the shoulder.
The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint, and
in a total shoulder replacement, both the ball (head of the humerus) and the
socket (glenoid) are replaced with prosthetic components. The surgery aims to
reduce pain, improve range of motion, and enhance overall shoulder function.
Here are
some key points about total shoulder replacement:
Indications:
Osteoarthritis: Degenerative wear and tear of the joint.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Autoimmune-related joint inflammation.
Post-traumatic Arthritis: Arthritis resulting from a previous injury.
Rotator Cuff Tear Arthropathy: Arthritis that develops secondary to a massive
rotator cuff tear.
Avascular Necrosis: Death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood
supply.
Surgical Procedure:
The surgeon makes an incision to access the
shoulder joint.
The damaged parts of the joint are removed.
The artificial components, which may be made
of metal, plastic, or a combination of materials, are implanted.
The new components are typically secured to
the bone with cement or press-fit methods.
Rehabilitation: Physical therapy is a crucial part of the recovery
process. Patients are usually guided through a rehabilitation program to regain
strength and range of motion. Full recovery may take several months, and it is
essential to follow the prescribed exercises and activity restrictions.
Risks and Complications:
As with any surgical procedure, there are
potential risks, including infection, blood clots, nerve injury, and
complications related to anesthesia.
Prosthetic components may wear out over time,
and revision surgery may be needed in the future.
Success and Outcomes:
Many patients experience significant pain
relief and improved function after total shoulder replacement.
The success of the surgery depends on various
factors, including the underlying condition, the patient's overall health, and
adherence to rehabilitation.






.png)