- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Ayurvedic Treatment
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
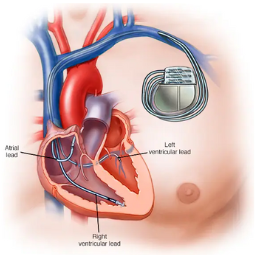
Pacemaker Implantation
Pacemaker Implantation is a medical procedure used to implant a small electronic device known
as a pacemaker into a patient's chest or abdomen. Pacemakers are primarily used
to regulate and control the heart's rhythm, ensuring that it beats at a normal
rate and rhythm. This procedure is typically performed by a cardiologist or an
electrophysiologist, a cardiologist specializing in heart rhythm disorders.
Here's an overview of pacemaker implantation:
Indications for Pacemaker Implantation: Pacemakers are used to treat various heart rhythm abnormalities,
including:
Bradycardia: A slow
heart rate, which can cause symptoms like dizziness, fatigue, and fainting. A
pacemaker helps maintain a normal heart rate.
Heart Block: A
condition in which the electrical signals in the heart's conduction system are delayed
or blocked, leading to slow or irregular heart rhythms.
Tachy-Brady Syndrome: A condition in which the heart alternates between slow and fast rhythms.
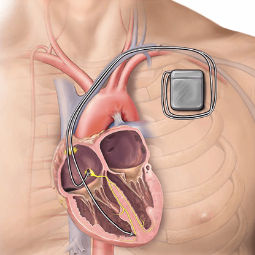
The Pacemaker Device: A
pacemaker consists of several components, including:
- Pulse Generator: This small metal or plastic device contains the battery and electronics. It generates electrical impulses to stimulate the heart.
- Leads: Thin, insulated wires that carry the
electrical impulses from the pulse generator to the heart muscle.
The Pacemaker Implantation Procedure: Pacemaker
implantation typically follows these steps:
- Preparation: The patient is prepared for the procedure by having an IV line inserted, electrodes placed for monitoring, and a local anesthetic applied to numb the area where the device will be implanted.
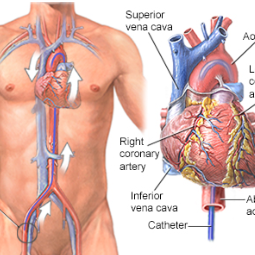
- Access Site: The device is usually implanted in the upper chest, just below the collarbone. An incision is made at the implantation site, and a small pocket is created for the pulse generator.
- Lead Placement: The leads are carefully threaded through a blood vessel from the implantation site to the heart. They are positioned in the heart chambers, depending on the specific rhythm disorder being treated.
- Testing: After the leads are secured, they are tested to ensure proper placement and function. The patient may be asked to move to assess the heart's response to the pacemaker's electrical signals.
- Securement: Once proper lead placement is confirmed, the leads are secured in place, and the pulse generator is connected to the leads.
- Closure: The incision is closed with sutures or staples, and a sterile dressing is applied.
- Programming: The
pacemaker is programmed to the patient's specific needs, ensuring it
delivers the appropriate electrical impulses to maintain a normal heart
rate.
After the Procedure: After pacemaker
implantation, the patient is monitored for a short period to ensure that the
device is functioning correctly. Most patients can return to their normal
activities within a few days, with some restrictions on heavy lifting and
overhead arm movements for a short time. Regular follow-up appointments are
scheduled to check the device's function, adjust settings if necessary, and
monitor the patient's overall heart health.
Pacemaker implantation is a safe and effective procedure that can
greatly improve the quality of life for individuals with heart rhythm
disorders. It ensures that the heart maintains a healthy and regular rhythm,
preventing symptoms associated with slow or irregular heartbeats.


.png)