- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
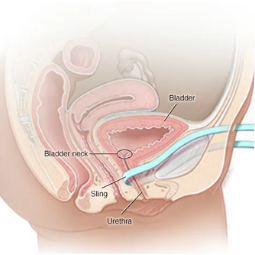
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Multispecialty
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
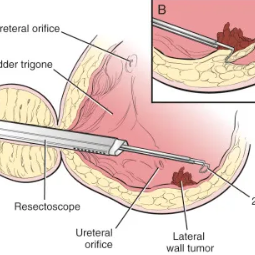
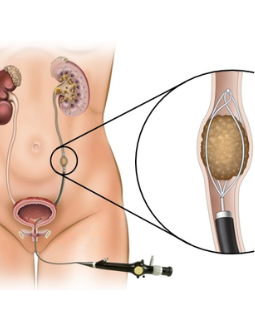
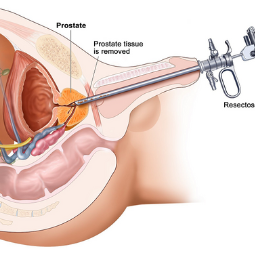
Transurethral Resection of a Bladder Tumor (TURBT)
Bladder Tumor Resection, also known as a Transurethral Resection of a Bladder Tumor (TURBT),
is a surgical procedure used to diagnose, stage, and treat bladder tumors,
particularly those that are suspected to be cancerous. Bladder tumor resection
is the most common procedure used to treat early-stage bladder cancer.
Here's an overview of the procedure:
Purpose:
- Diagnostic TURBT: One of the primary purposes of TURBT is to diagnose bladder tumors. It involves the removal of a small piece of tissue (biopsy) from the bladder lining for examination under a microscope. This helps determine if the tumor is cancerous, its stage, and its type.
- Therapeutic TURBT: In cases where the bladder tumor is small and localized, TURBT can also be used as a treatment method to remove the tumor. For more advanced bladder cancer, additional treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or radiation therapy, may be required.
Procedure:
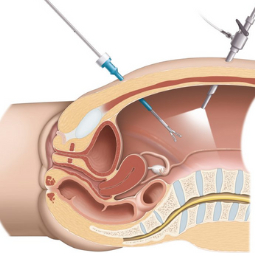
- TURBT is typically performed under general or regional anesthesia. The patient may be positioned in a lithotomy (legs-up) position.
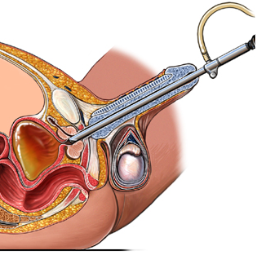
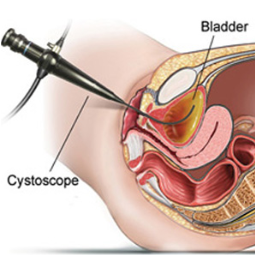
- A cystoscope, a thin tube with a camera and a light on the end, is inserted through the urethra and into the bladder. This allows the urologist to visualize the inside of the bladder.
- Small surgical instruments are passed through the cystoscope, and
the surgeon carefully removes or resects the bladder tumor. The tumor is
then sent to a pathologist for examination.
Staging: If the
tumor is found to be malignant, the pathologist can provide important information
about its stage and grade. This information helps determine the extent of the
cancer's spread within the bladder, which can guide further treatment
decisions.
Recovery: Recovery after TURBT is generally quick.
Most patients can go home the same day or the day after the procedure. Some
temporary discomfort or mild urinary symptoms may be experienced after the
procedure.
Risks and Complications: Common
risks and complications associated with TURBT may include bleeding, infection,
bladder perforation, or, in some cases, tumor recurrence.
TURBT is a valuable procedure for diagnosing and treating bladder
tumors, particularly for early-stage bladder cancer. If cancer is confirmed,
the findings from TURBT play a crucial role in determining the appropriate
treatment plan, which may involve further surgery, radiation therapy,
chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these treatments. The choice
of treatment depends on the specific type and stage of bladder cancer.


.png)