- Home
- About
- Hospitals
-
Treatments
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Knee Replacement
- Carpal Tunnel Release
- Rotator Cuff Repair
- Meniscus Repair / Meniscectomy
- Total Hip Replacement (THR)
- Total Shoulder Replacement
- Arthroscopy
- Ligament Reconstruction
- Spinal Fusion
- Discectomy
- Laminectomy
- Spinal Decompression
- Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty
- Fracture Repair
- ACL Reconstruction
- Tendon Repair
- Osteotomy
- Amputation
- Pediatric and Adult Cardiac
- Neuroscience
- Oncology
- Nephrology & KTP
- Gastroenterology & Hepatobiliary
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Infertility
- Dental & Maxillofacial
- Plastic & Cosmetic Surgery
- Rhinoplasty
- Blepharoplasty (Eyelid Surgery)
- Facelift (Rhytidectomy)
- Breast Augmentation (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Reduction (Mammoplasty)
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy)
- Liposuction
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy Tuck)
- Brazilian Butt Lift (BBL)
- Lip Augmentation
- Breast Reconstruction
- Cleft Lip and Palate Repair
- Scar Revision
- Burn Reconstruction
- Botox Injection
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Endocrinology
- General and Minimal Invasive Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Urology
- General Medicine
- Multispecialty
- Orthopedic & Spine
- Doctors
- Contact Us
Endovascular Coiling and Clipping
Endovascular coiling and
clipping are two techniques used to treat cerebral aneurysms, which are
weakened areas in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain that can balloon and
potentially rupture. Both procedures aim to prevent the risk of an aneurysm rupture
and subsequent bleeding into the brain, a condition known as a subarachnoid
hemorrhage.
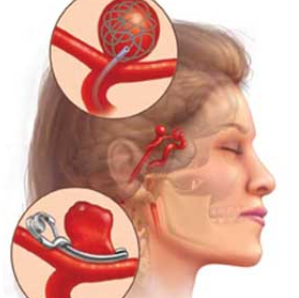
Cerebral Aneurysms:
Definition: A cerebral aneurysm is a bulging, weakened area in
the wall of a blood vessel in the brain.
Risk of Rupture: Aneurysms may rupture, leading to subarachnoid
hemorrhage, a serious and potentially life-threatening condition.
Endovascular Coiling: A catheter is threaded through the blood vessels
from a distant access point, usually the femoral artery in the groin, to the
site of the aneurysm in the brain.
Soft platinum coils are delivered through the catheter and released into the aneurysm.
The coils induce blood clotting
within the aneurysm, promoting the formation of a stable blood clot that seals
off the aneurysm from the circulation.


.png)